Fundamentals about playing bullet force hack
FPS gaming is a special game controller to fit your demands of a firefight that are digital. Although FPS gamers vary widely in their opinion of what makes a great gaming experience, a bunch of ‘musts’ exist for an FPS technology to provide an Wonderful firefight First the controller Feel must look and behave like a real gun. Research has revealed that must look and act the part. Balls on the end of firearms and Nerf guns could be fine for some, but boys and men love guns suits this foundation need. During the first few Instances of enjoying with an FPS game, it is tough to respond to things that are unexpected.
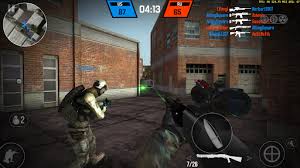
If it does not have iron sights its own saying please does not aim me. Since you would not purchase a gun controller that does not wish to be aimed, consider this your overriding criteria. Does the Controller rely on buttons for movement or have over 6 buttons? Then this is if aiming requirements are satisfied. Our research has demonstrated that although gaming companies want their customers to embrace button management schemes to their financial motives, a 6DOF integration which brings the game to life will prevail with clients. Before investing in a gun control be certain how moves you need to move from the game.
Any game seriously fulfilling with the requirement of FPS Gamers desire to be immersed in the game would not have. Simple, give it a pass. When you consider Buying a gun control, above when implemented, the standards may help you determine whether the item is worth not, or your time. I have always seen FPS gamers as the most alert gamers out there. Usually, there are some types of grace period when playing RPGs or RTS games where you are able to take a 5 minute breather and only plan on what you will need to do. I’m not saying that RPG gamers or RTS gamers get it simple; they both have their own challenges. FPS gamers are accustomed to playing under pressure. FPS first person shooter gamers gain a feeling of alertness and improved dexterity due to the game mechanics.
Pool Live Tour Hack require you to maintain a first person view like you are actually walking within the game and shoot anything that threatens your existence. Needless to say, if you are new to fps games, it is tough to have a shot. Not to mention, the strain will kick in and your cursor would be missing your enemy you wind up shooting everywhere.





 A cargo carrier can be useful in so many unique situations. Additionally, there are different kinds of containers such as a hard case box, bag, or basket with a web. Whether you need more storage to transfer things in your car or truck or need more space for a summer road trip, a roof freight container is an excellent solution. This is particularly true if roof rack cross bars have been installed on the vehicle, truck or suv.
A cargo carrier can be useful in so many unique situations. Additionally, there are different kinds of containers such as a hard case box, bag, or basket with a web. Whether you need more storage to transfer things in your car or truck or need more space for a summer road trip, a roof freight container is an excellent solution. This is particularly true if roof rack cross bars have been installed on the vehicle, truck or suv. When searching for a crib mattress for your tyke, you ought to guarantee that no harming items or chemicals are found in any of the 4 key parts of the mattress. These 4 key segments are 1 the center, 2 the cushioning, 3 the fire resistant item, and furthermore 4 the ticking. Ordinarily regular crib bed mattress or ones produced using 100% common items make utilization of secure, characteristic items over every one of the 4 components of the mattress. As you explore think about pads, search for ones with an innerspring center or a center produced using an all-normal material, for example, cotton, woolen or all-common latex. An innerspring center comprises of steel springtime’s, effortlessly you would likely find in your own mattress. On the off chance that obtaining a crib mattress with a center produced using cotton, guarantee to pick normal as customary cotton can be treated with chemicals.
When searching for a crib mattress for your tyke, you ought to guarantee that no harming items or chemicals are found in any of the 4 key parts of the mattress. These 4 key segments are 1 the center, 2 the cushioning, 3 the fire resistant item, and furthermore 4 the ticking. Ordinarily regular crib bed mattress or ones produced using 100% common items make utilization of secure, characteristic items over every one of the 4 components of the mattress. As you explore think about pads, search for ones with an innerspring center or a center produced using an all-normal material, for example, cotton, woolen or all-common latex. An innerspring center comprises of steel springtime’s, effortlessly you would likely find in your own mattress. On the off chance that obtaining a crib mattress with a center produced using cotton, guarantee to pick normal as customary cotton can be treated with chemicals. The program unblocked game will certainly additionally be a very easy little internet game that is unblocked. Making use of the renovation within the general populace have actually currently been exceptionally educated started instinct as well as later turned up by creating the idea of these unblocked game game-which created the usage of numerous suggestions as their clients. It was likely round the reasons that with the enhancement of the web along with the web, the applications ended up being considerably best-in university which produced the idea of program unblocked game ended up to end up being true. One more development in the region of program diversion began whilst the idea of plan tasks wound up to become considered where the use of varied offered renovations to develop these activities began. Making use of the using costly, in addition to java, in the area of web unblocked game produced these unblocked game rips off game made complex, maligned them the a lot more interesting for the members.
The program unblocked game will certainly additionally be a very easy little internet game that is unblocked. Making use of the renovation within the general populace have actually currently been exceptionally educated started instinct as well as later turned up by creating the idea of these unblocked game game-which created the usage of numerous suggestions as their clients. It was likely round the reasons that with the enhancement of the web along with the web, the applications ended up being considerably best-in university which produced the idea of program unblocked game ended up to end up being true. One more development in the region of program diversion began whilst the idea of plan tasks wound up to become considered where the use of varied offered renovations to develop these activities began. Making use of the using costly, in addition to java, in the area of web unblocked game produced these unblocked game rips off game made complex, maligned them the a lot more interesting for the members. The muslim mind coverings called hijabs are utilized by tens of thousands of Muslim women throughout the world. Though their principal reason for utilizing hijabs is spiritual, as Islam allows girls to cover their minds so as to promote modesty and decency, but individuals who use them also reap a couple different advantages from its own use. Because these scarves are utilized in a manner that covers the mind completely in about a few layers in addition to partly covers the face by both sides and bottom, they are a terrific way to shield the face and hair from unpleasant character elements like warmth, sun rays and dust from the summers in addition to snow and rain in the winters.
The muslim mind coverings called hijabs are utilized by tens of thousands of Muslim women throughout the world. Though their principal reason for utilizing hijabs is spiritual, as Islam allows girls to cover their minds so as to promote modesty and decency, but individuals who use them also reap a couple different advantages from its own use. Because these scarves are utilized in a manner that covers the mind completely in about a few layers in addition to partly covers the face by both sides and bottom, they are a terrific way to shield the face and hair from unpleasant character elements like warmth, sun rays and dust from the summers in addition to snow and rain in the winters.
 Grocery shopping can be a task for many people. It is an event that can cause frustration should you not enjoy shopping. The errand cannot be ignored and when food supplies are low, it is time. This report comprises some grocery shopping strategies. The grocery shopping is completed with a listing. Keep a list of the things that you require. Before heading out to the shop as you run out or become low you can catch the listing. It is much better to have more of something than not enough. You can stock up on sundries that you use, for those who have storage space in your cabinets or pantry, and you will have the ability to earn frequent trips to the grocery store.
Grocery shopping can be a task for many people. It is an event that can cause frustration should you not enjoy shopping. The errand cannot be ignored and when food supplies are low, it is time. This report comprises some grocery shopping strategies. The grocery shopping is completed with a listing. Keep a list of the things that you require. Before heading out to the shop as you run out or become low you can catch the listing. It is much better to have more of something than not enough. You can stock up on sundries that you use, for those who have storage space in your cabinets or pantry, and you will have the ability to earn frequent trips to the grocery store.
 Making ourselves pretty is a lot more excellent from all the various other works it comes under numerous points when if you observe the modifications on your skin certainly you will certainly really feel bad of that and now no should ignore or accept that you can merely go through the various points and also modifications you need on the face or other areas of the skin, which one of the most of the celebrities do. Once if they enter into the
Making ourselves pretty is a lot more excellent from all the various other works it comes under numerous points when if you observe the modifications on your skin certainly you will certainly really feel bad of that and now no should ignore or accept that you can merely go through the various points and also modifications you need on the face or other areas of the skin, which one of the most of the celebrities do. Once if they enter into the 



 Folks are usually turned off by the notion of purchasing used cars. They think it is a compromise on the quality to save some dollars. Read on to take a peek. A Car with designs and features provide a fine maintenance and experience. The reason why a car is not owned by each one with all features is the digits that are tagged as that car’s purchase price. Cars or another car or for that matter anything with greater appears and features costs more. Some could make a person’s bank account cave. However, the practical Uses of a car cannot be discounted. So if you cannot afford to buy a car would be to purchase a used one. You can save and own a vehicle by opting to get a car.
Folks are usually turned off by the notion of purchasing used cars. They think it is a compromise on the quality to save some dollars. Read on to take a peek. A Car with designs and features provide a fine maintenance and experience. The reason why a car is not owned by each one with all features is the digits that are tagged as that car’s purchase price. Cars or another car or for that matter anything with greater appears and features costs more. Some could make a person’s bank account cave. However, the practical Uses of a car cannot be discounted. So if you cannot afford to buy a car would be to purchase a used one. You can save and own a vehicle by opting to get a car. Seascape photography is essentially considered as an exceptionally unusual occupation. Be that as it may, the era of today shows component of enthusiasm for this vocation therefore all things thought about a large portion of the youths take this calling as a major examination for themselves. And each of the adolescents should provide absolute finest to their holder. They are prepared to check out every opportunity keeping in mind the end objective to accomplish their objective. Individuals unquestionably need to acquire a part of the most effective and remarkably proficient photographers, who have parcel of energy for their work with a certain end goal to catch a section of the vital occasions like Seascape in one’s life. These pictures ought to be rather lately consummate in light of that you at some point obtain hitched just as soon as therefore you would need to capture each service in the most excellent way with the objective that you could then prize these mins after the reality in your life.
Seascape photography is essentially considered as an exceptionally unusual occupation. Be that as it may, the era of today shows component of enthusiasm for this vocation therefore all things thought about a large portion of the youths take this calling as a major examination for themselves. And each of the adolescents should provide absolute finest to their holder. They are prepared to check out every opportunity keeping in mind the end objective to accomplish their objective. Individuals unquestionably need to acquire a part of the most effective and remarkably proficient photographers, who have parcel of energy for their work with a certain end goal to catch a section of the vital occasions like Seascape in one’s life. These pictures ought to be rather lately consummate in light of that you at some point obtain hitched just as soon as therefore you would need to capture each service in the most excellent way with the objective that you could then prize these mins after the reality in your life.
 Payday loan is the fastest and the simplest solution to a brief term fiscal matter. This is as it is likely to locate financing within the afternoon, get accepted even in the event that you have a bad credit report, or discover the money via your saving accounts no questions ask! You see payday loans operate just like every other loan vehicles however. The payday loans work is not tough to comprehend. The debtor has the choice to utilize the loan online, over the phone, or even in the lender’s office. The debtor will be asked for 3 prerequisites: evidence of employment that changes from company to company. Sometimes the business needs that the creditors ought to be frequently employed on a certain time period at the specific same occupation, should be at least 18 years old and also busy savings account.
Payday loan is the fastest and the simplest solution to a brief term fiscal matter. This is as it is likely to locate financing within the afternoon, get accepted even in the event that you have a bad credit report, or discover the money via your saving accounts no questions ask! You see payday loans operate just like every other loan vehicles however. The payday loans work is not tough to comprehend. The debtor has the choice to utilize the loan online, over the phone, or even in the lender’s office. The debtor will be asked for 3 prerequisites: evidence of employment that changes from company to company. Sometimes the business needs that the creditors ought to be frequently employed on a certain time period at the specific same occupation, should be at least 18 years old and also busy savings account.


